A threatening seaweed
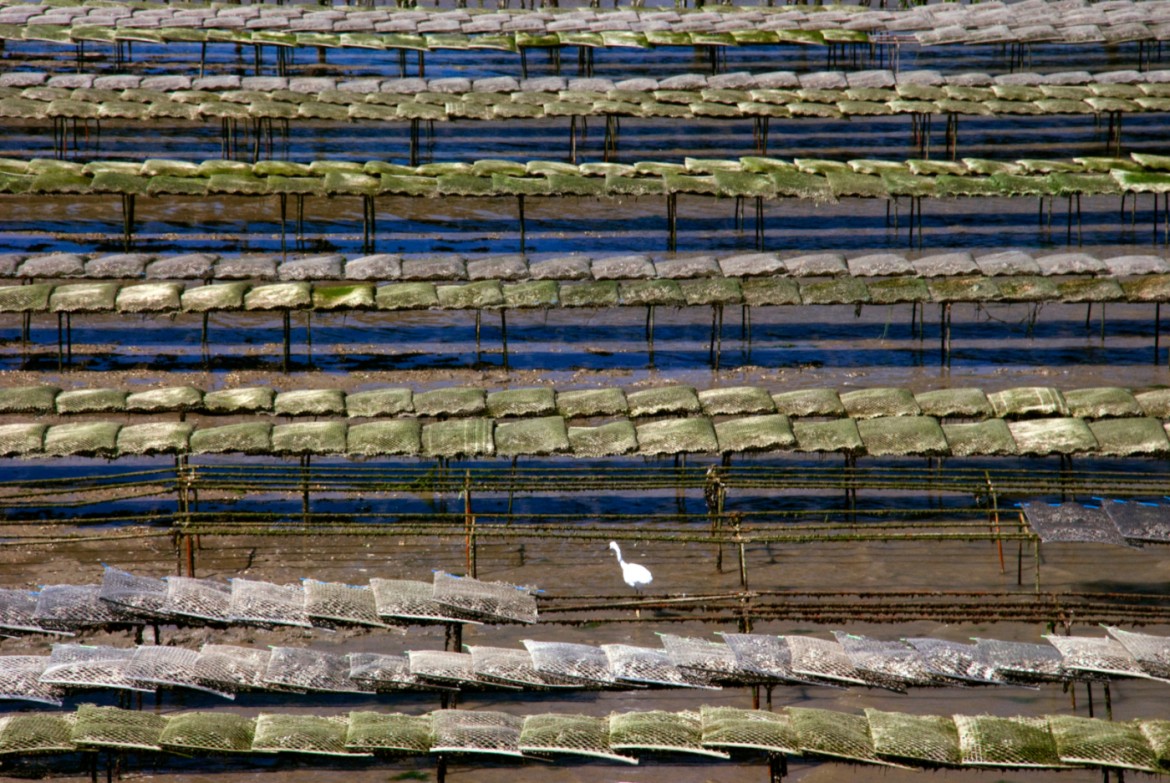
Maria and Jean-Michel Douet are standing on hot coals. In their cabin of the Cap-Ferret, the two young oyster famers are waiting for a fateful text message. « Tests performed in Arguin and in the Bassin came out positive for oyster and mussels. Everything is shut down. Courage and see you soon. » In oyster farming language this means disaster. Especially since the same scenario has been happening over and over again for the past five years and threatens 380 farms working on the 780 hectares of oyster beds yielding between 8,000 and 10,000 tons of oysters a year.
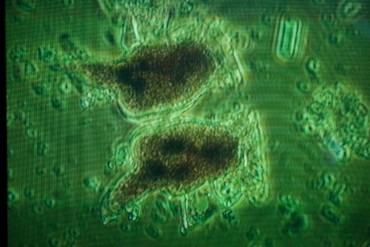
Dinophysis, a natural but toxic micro-alga seems to be the culprit. It releases a toxin which causes diarrhea in oyster eaters who ingest it. Oysters are water filters. They absorb and reject liters of sea water on a daily basis. They are thus the first to be contaminated. Even if this unwelcomed alga has never caused a single fatality, the European Union imposes the famous mouse biological test (see in chapter 2) in the name of the holly precaution principle, making oyster farmers hostages of the death, or survival of the little white mice…
After years of research, the teams of the Institut français de recherche pour l’exploitation de la mer (Ifremer – French Institute for Exploitation of the Sea) have established a list of elements coinciding with the apparition of the dinophysis. « Spring unfortunately combines a number of events which seem to perfectly suit the alga, explains Roger Kantin, head of the Arcachon Ifremer station. Increasing daylight period, rise in water temperature (from 17°C) combined with fresh water influx carrying nitrates and phosphates from rivers which flow into the Bassin d’Arcachon. » As for the last two elements, they seem to be clearly resulting from human activity.